WhiteHaX AI-ASM Platform
Continuously Verify AI-deployment before it becomes a Business Risk
Overview
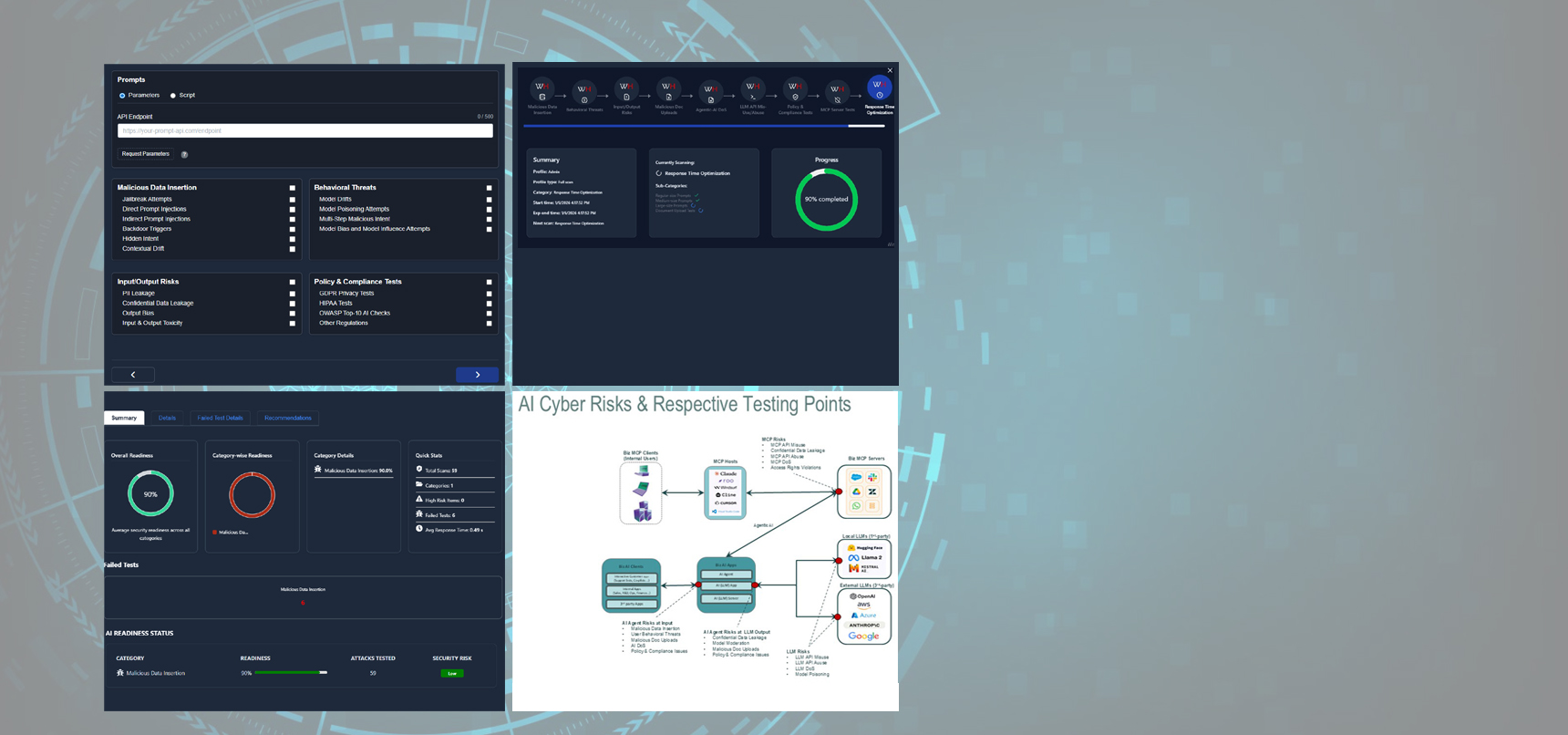
WhiteHaX AI-ASM Platform is an enterprise-grade, automated testing and validation platform designed to harden Generative AI and Large Language Model (LLM) applications against a comprehensive spectrum of security threats and compliance risks. By simulating thousands of sophisticated adversarial attacks and policy violations, WhiteHaX AI-ASM provides developers and security teams with actionable intelligence to identify AI-specific vulnerabilities, prevent data leaks, and ensure regulatory adherence before deployment.
The WhiteHaX AI-ASM verifies the full-scale cyber-readiness of Agentic-AI deployments (including those using RAG) while allowing businesses to measure AI responsiveness and performance through average response time measurement of their AI applications.
2. Technical Specifications
| Category | Specification |
|---|---|
| Deployment Model | SaaS (Cloud-Hosted) Management with On-Premise WhiteHaX App (Win, Linux, MaCOS) |
| Integration | REST API, CLI, CI/CD Pipelines (including SAST/DAST integration) |
| Testing Volume | Capable of executing Hundreds of Thousands of unique test cases per hour per target system. |
| Attack Library | Curated and continuously updated library of 1,000,000+ malicious prompts; 5,000+ malicious docs; Ability to generate custom prompts using Semantically-trained internal LLMs, Hundreds of testing scenarios. |
| Customization | Full customization of prompts using training inputs; Expected results verification as per deployed business-application and other params |
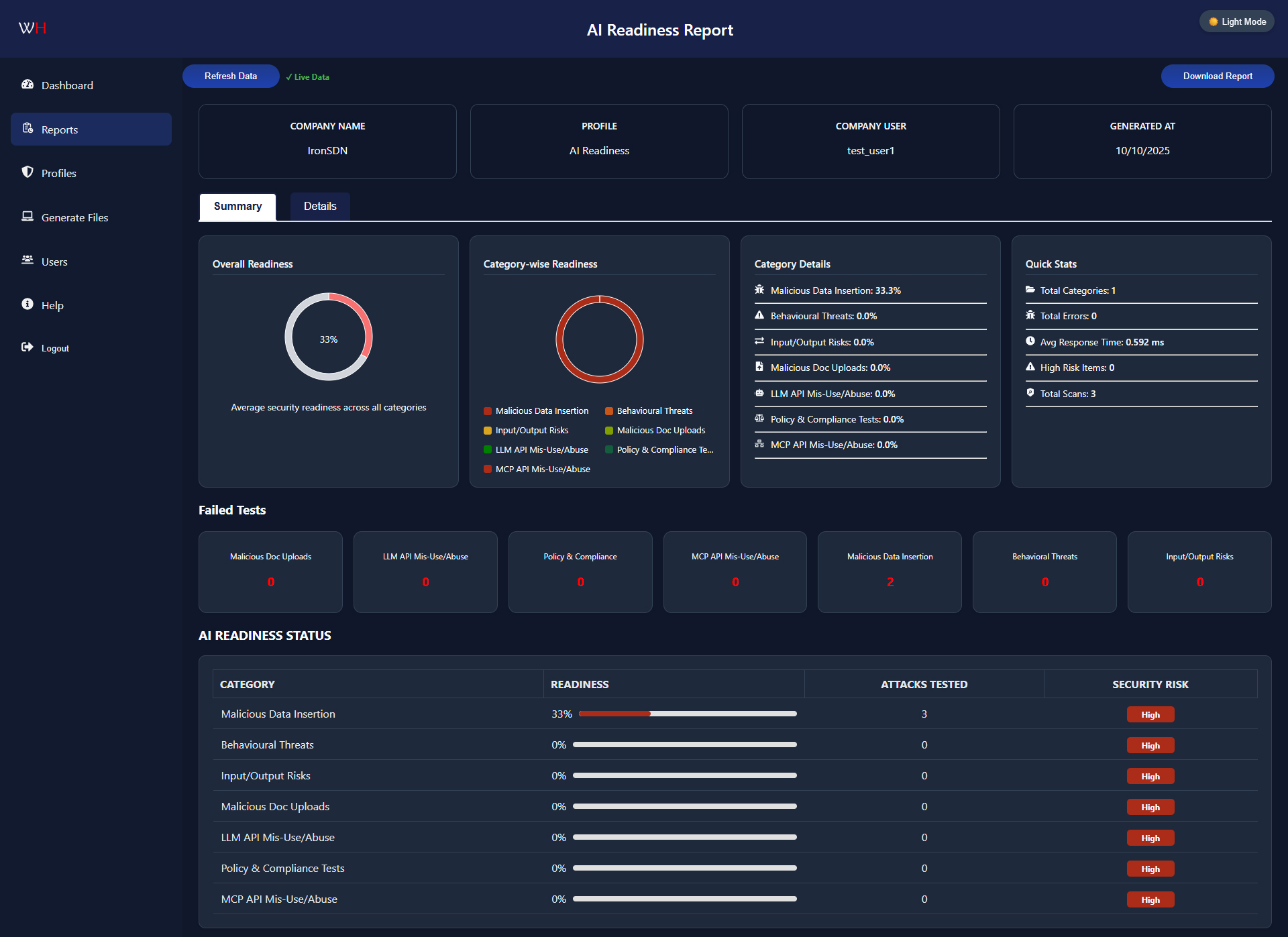
| Report Generation | Detailed PDF/HTML reports with failed prompts/docs and other details, remediation guidance, and compliance gaps. |
| Dashboard | Centralized web dashboard for managing tests, viewing results, and tracking trends over time. |
3. Target Users
- Security & Red Teams: Proactively find and remediate critical vulnerabilities in AI deployments.
- Compliance & Risk Officers: Audit AI systems for adherence to internal policies and external regulations.
- AI Application Developers :Integrate security testing into the development lifecycle (DevSecOps) – along with SAST/DAST tools.
- Product Managers: Ensure customer-facing AI features are safe, reliable, and trustworthy.
4. Benefits
- Proactive Security: Shift-left security testing to identify vulnerabilities before they reach production.
- Compliance Confidence: Automate evidence gathering for audits and ensure continuous compliance.
- Protect Brand Reputation: : Prevent high-profile security incidents and biased outputs that cause reputational damage.
- Reduce Risk:: Significantly lower the risk of AI-related data breaches, model theft, confidential data leakage and system compromise via AI endpoints.
- Save Time & Resources: Automate thousands of tests that to continuously validated AI business deployments.
5. Supported Use-Cases & Deployment Types
WhiteHaX is designed to test a wide array of AI deployments, including following example use-cases:
- Public-Facing Chatbots & Assistants
- Internal Copilots and Productivity Tools
- AI-Powered Search and Retrieval Systems
- Code Generation Assistants (e.g., GitHub Copilot alternatives)
- Content Generation and Marketing Platforms
- Research & Development Applications in variety of industries
- AI APIs serving multiple downstream applications
Key Features & Capabilities
WhiteHaX's AI testing modules are organized into Nine Core pillars of AI security:
- Direct Prompt Injection: Systematically attempts to override initial system prompts to force unintended model behavior.
- Indirect (Jailbreak) Attacks: Tests thousands of sophisticated jailbreak techniques (e.g., DAN, character 扮演, encoded instructions) designed to bypass ethical safeguards.
- Backdoor Triggers: : Injects hidden triggers and anomalous patterns into seemingly benign inputs to test for unexpected and malicious outputs.
- Model Hijacking: Attempts to subvert the AI's intended task to perform a hidden, malicious objective.
- Model Drift Simulation: Monitors and measures output consistency over time to detect performance degradation and concept drift.
- Model Poisoning Attempts: Simulates training data poisoning attacks by testing how the model responds to inputs designed to corrupt future learning or fine-tuning cycles.
- Multi-Step Malicious Intent: Executes complex, multi-prompt attack sequences that appear harmless individually but achieve a malicious goal collectively.
- Bias & Influence Detection: Probes the model for inherent biases related to demographics, ideology, and culture. Tests susceptibility to persuasion and influence campaigns.
- PII Leakage Detection: : Inputs prompts designed to trick the model into revealing sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII) from its training data or context window.
- Confidential Data Leakage: Tests for accidental exposure of proprietary business data, intellectual property, or confidential internal information.
- Output Bias Analysis: Systematically audits outputs for fairness, identifying discriminatory language or unfair recommendations across protected classes.
- Toxicity Analysis: Evaluates both user inputs and AI outputs for toxic, hateful, explicit, or harassing content.
- File Format Fuzzing: Tests the entire document processing pipeline with a vast library of maliciously crafted files, including:
- MS-Office Docs (Word, Excel, PPT etc.): Macros, embedded objects, hidden content, and exploit code.
- PDFs: :Malicious embedded objects such as images, hyperlinks, and corrupted structures.
- Images (JPG, PNG, SVG, etc.): Steganography, pixel flood attacks, malicious SVG scripts, and prompt injections embedded in image metadata.
- QR Codes: QR codes containing malicious URLs, prompt injections, or other exploit code.
- Invalid API Request Flooding: Stress-tests API endpoints with malformed requests, high-volume traffic, and various encoding attacks.
- Key/Token Abuse Simulation: : Tests authentication and rate-limiting controls by simulating token theft, replay attacks, and permission bypass attempts.
- Anomalous Access Pattern Detection: Generates traffic patterns indicative of scraping, data exfiltration, and brute-force attacks.
- Access Rights Abuse: Attempts to access prompts, data, or functionalities outside the scope of a given user's API key permissions.
- Resource Exhaustion: Agentic-AI resource exhaustion can lead to unresponsive AI apps. Verify if your Agentic-AI can handle large number of Concurrent Requests-per-Sec simultaneously with large load of user responses.
- Cost Amplification:Cost of LLM requests and responses can add up very quickly, if AI app doesn’t throttle back-end LLM usage. Stress-test Agentic-AI deployment to ensure that both request handling and request throttling for back-end LLM are handled without cost overrun.
- Memory Exhaustion: : By varying payload size along with number of simultaneous requests, attackers can cause potential memory exhaustion of the AI-app and make it unresponsive. WhiteHaX can verify various load sizes with simultaneous requests for ensuring AI-app stress test limits.
- Token Overflow & Rate Limit Bypass: By varying user request parameters and attacker can cause denial-of-service on your Agentic-AI. Test token overflow through various test strategies such as IP Rotation, Endpoint Variation and Parameter Mutation to ensure your Agentic-AI infrastructure can thwart this types of attacks.
- GDPR Privacy Tests: Validates the system's ability to handle Right to Be Forgotten (erasure) requests and prevents PII leakage as mandated by GDPR.
- HIPAA Tests: Specifically tests for scenarios that could lead to the exposure of Protected Health Information (PHI).
- OWASP Top-10 for LLM Checks: Full test suite aligned with the Open Web Application Security Project's top vulnerabilities for LLMs (e.g., LLM01: Prompt Injection, LLM02: Data Leakage).
- Custom Regulatory Frameworks: Allows for the creation of custom test cases to meet specific industry or regional regulations (e.g., CCPA, PCI DSS, EU AI Act).
- Response time for Prompt Inputs: Measure avg response time of input prompts and improve it for optimal response by allocating necessary resources.
- Response time of Document Processing: Measure avg response time of uploaded docs for better throughput.
- Overall System Performance: : Track AI system’s performance trend over time to monitor for degradation or improvements.
- Protocol Violation: Generate MCP protocol violations to see if your MCP services can handle attempts to bypass security controls.
- MCP Tool Abuse: Maks sure your MCP service handles tools abuse that can result in service crash, disclosure of private or confidential info, service subversion or other errors.
- Resource Exhaustion: : Generate enough MCP concurrent requests simultaneously with protocol requests and tool requests to stress test resource exhaustion on resource capacity of your MCP service.
- Memory Leak:Ensure MCP service doesn’t cause memory leakage by iterating requests over and over with same or varying requests parameters.
- Session Hijack: : Verify that MCP service is not prone to potential session hijack by stress testing number of simultaneous sessions.
- Additional MCP Tests: WhiteHaX AI-ASM also allows you to verify your MCP service against other MCP specific attacks such as Context Overflow or Malicious Tool insertion through generating MCP abusive traffic.
Contact: For more information, please visit www.WhiteHaX.com or contact sales team at sales@WhiteHaX.com.
Proprietary and copyrighted material of IronSDN, Corp. ©️ Copyright 2022. All rights reserved.
For more information, visit www.WhiteHaX.com